New classes are introduced to represent HTTP messages and their associated bodies. The parser interface is reworked to use CRTP, error codes, and trait checks. New classes: * basic_headers Models field/value pairs in a HTTP message. * message Models a HTTP message, body behavior defined by template argument. Parsed message carries metadata generated during parsing. * parser Produces parsed messages. * empty_body, string_body, basic_streambuf_body Classes used to represent content bodies in various ways. New functions: * read, async_read, write, async_write Read and write HTTP messages on a socket. New concepts: * Body: Represents the HTTP Content-Body. * Field: A HTTP header field. * FieldSequence: A forward sequence of fields. * Reader: Parses a Body from a stream of bytes. * Writer: Serializes a Body to buffers. basic_parser changes: * add write methods which throw exceptions instead * error_code passed via parameter instead of return value * fold private member calls into existing callbacks * basic_parser uses CRTP instead of virtual members * add documentation on Derived requirements for CRTP impl/http-parser changes: * joyent renamed to nodejs to reflect upstream changes
#The World’s Fastest and Most Secure Payment System
What is Ripple?
Ripple is the open-source, distributed payment protocol that enables instant payments with low fees, no chargebacks, and currency flexibility (for example dollars, yen, euros, bitcoins, or even loyalty points). Businesses of any size can easily build payment solutions such as banking or remittance apps, and accelerate the movement of money. Ripple enables the world to move value the way it moves information on the Internet.
What is a Gateway?
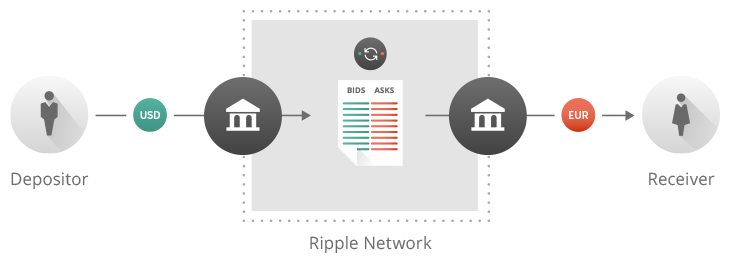
Ripple works with gateways: independent businesses which hold customer deposits in various currencies such as U.S. dollars (USD) or Euros (EUR), in exchange for providing cryptographically-signed issuances that users can send and trade with one another in seconds on the Ripple network. Within the protocol, exchanges between multiple currencies can occur atomically without any central authority to monitor them. Later, customers can withdraw their Ripple balances from the gateways that created those issuances.
How do Ripple payments work?
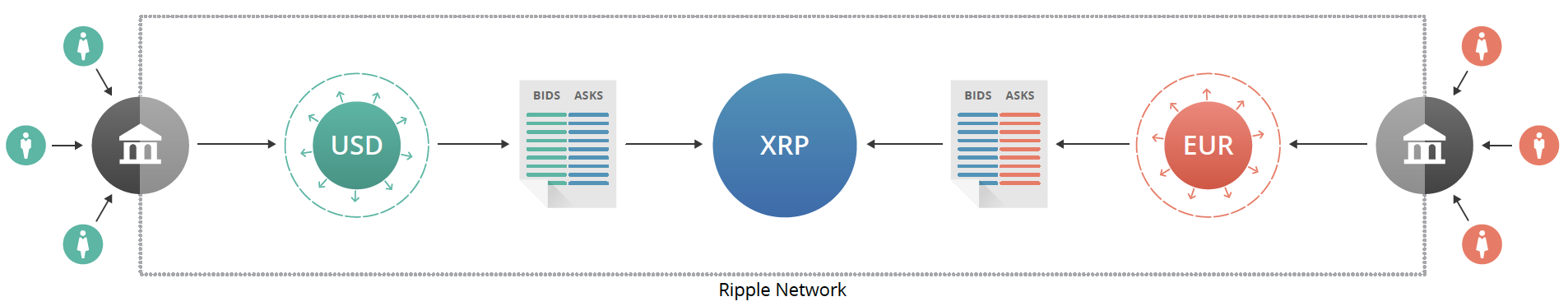
A sender specifies the amount and currency the recipient should receive and Ripple automatically converts the sender’s available currencies using the distributed order books integrated into the Ripple protocol. Independent third parties acting as market makers provide liquidity in these order books.
Ripple uses a pathfinding algorithm that considers currency pairs when converting from the source to the destination currency. This algorithm searches for a series of currency swaps that gives the user the lowest cost. Since anyone can participate as a market maker, market forces drive fees to the lowest practical level.
What can you do with Ripple?
The protocol is entirely open-source and the network’s shared ledger is public information, so no central authority prevents anyone from participating. Anyone can become a market maker, create a wallet or a gateway, or monitor network behavior. Competition drives down spreads and fees, making the network useful to everyone.
###Key Protocol Features
-
XRP is Ripple’s native [cryptocurrency] (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptocurrency) with a fixed supply that decreases slowly over time, with no mining. XRP acts as a bridge currency, and pays for transaction fees that protect the network against spam.
-
Pathfinding discovers cheap and efficient payment paths through multiple order books allowing anyone to trade anything. When two accounts aren’t linked by relationships of trust, the Ripple pathfinding engine considers intermediate links and order books to produce a set of possible paths the transaction can take. When the payment is processed, the liquidity along these paths is iteratively consumed in best-first order.

-
Consensus confirms transactions in an atomic fashion, without mining, ensuring efficient use of resources.
###Join The Ripple Community
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Transact on the fastest payment infrastructure | Build Imaginative Apps | Contribute to the Ripple Protocol Implementation |
#rippled - Ripple P2P server
This is the repository for Ripple's rippled, reference P2P server.
###Build instructions:
###Setup instructions:
###Issues
Repository Contents
./bin
Scripts and data files for Ripple integrators.
./build
Intermediate and final build outputs.
./Builds
Platform or IDE-specific project files.
./doc
Documentation and example configuration files.
./src
Source code directory. Some of the directories contained here are external repositories inlined via git-subtree, see the corresponding README for more details.
./test
Javascript / Mocha tests.
License
Ripple is open source and permissively licensed under the ISC license. See the LICENSE file for more details.
###For more information:
- Ripple Wiki - https://ripple.com/wiki/
- Ripple Primer - https://ripple.com/ripple_primer.pdf
- Ripple Primer (Market Making) - https://ripple.com/ripple-mm.pdf
- Ripple Gateway Primer - https://ripple.com/ripple-gateways.pdf
- Consensus - https://wiki.ripple.com/Consensus
Copyright © 2015, Ripple Labs. All rights reserved.
Portions of this document, including but not limited to the Ripple logo, images and image templates are the property of Ripple Labs and cannot be copied or used without permission.